Overview
Have you ever walked into your local drug store just to grab an allergy medicine and became instantly overwhelmed with all the choices in front of you? In this guide, we will hopefully simplify your options and give you a better idea of just what medication is the best choice for you.
What Is Histamine?
Histamine plays a central role in the allergic response and it's main purpose is not to simply cause the symptoms we hate so much (although it feels like that sometimes!). It's effects on the blood vessels in our body and in our airways is what usually causes the most grief. Histamine also has a major role in the release of stomach acid and the release of neurotransmitters in the brain.
There are numerous histamine receptors, but this article will focus on H1 receptors. All the antihistamine medications that are indicated for allergies are H1 antagonists or simply "antihistamines".
When released, histamine causes some of the following effects:
- Vasodilation (dilating the blood vessels) - This is what causes a majority of the nasal symptoms you experience, most commonly that congested nose.
- Cardiac effects - Something we are not usually as aware of when our allergies hit us, but histamine influences both how hard our heart contracts and how fast it pumps.
- Contraction of Smooth Muscle - Smooth muscle is found everywhere in the body including in our airways. This causes the symptoms of wheezing and coughing.
- Itching - Histamine release also causes itching and redness. The mechanism behind this response is somewhat complicated, but it involves increasing the permeability of small vessels and the separation of skin cells.
Antihistamines
So we take antihistamines to negate the effects of histamine on the body. There are NUMEROUS antihistamines available for purchase. They are typically divided into generations, both first and second.
The first generation antihistamines are typically short acting and sedating (due to their ability to enter your brain and cause drowsiness) while the second generation antihistamines tend to be longer lasting but perhaps not quite as effective in cases of a severe allergic reaction like a bee sting.
It is interesting to note that while the first generation antihistamines such as Benadryl (diphenhydramine) is known to cause sedation, it can actually stimulate some people, most often children.
The sedation side effect of the first generation antihistamines has led them to be marketed as sleep aids as well. Most over the counter sleep aids (Sominex, Nyquil) just contain sedating antihistamines.
First Generation Antihistamines
The first generation, as mentioned before, is noted for it's quick onset of action, short duration of action, sedation and effectiveness for use in allergic reaction situations. There are actually many different classes within the first generation antihistamines (e.g. Ethanolamines, Piperazines etc) but we will just stick some the general relationship between all of them. We will note interesting comments and uses for the various drug in the chart and section below.
Here is a chart of common first generation antihistamines (There are a lot!)
First Generation Antihistamine Comparison Chart
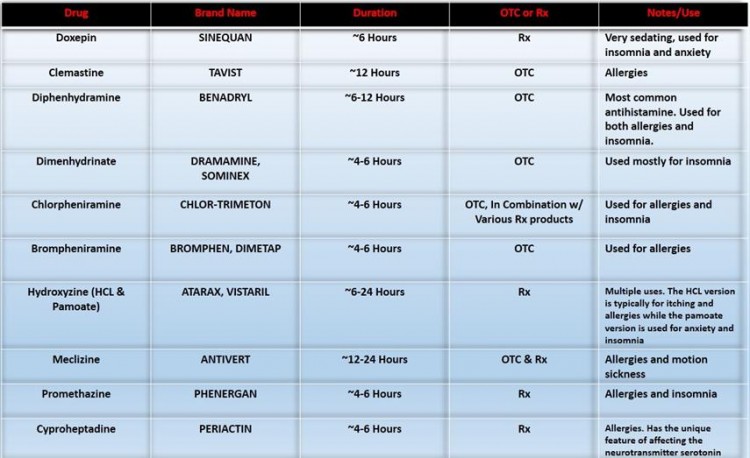
Comments On First Generation Antihistamines
- Doxepin - Doxepin is a prescription antihistamine and is almost never used just for allergies. It's an extremely strong H1 antagonist that easily causes drowsiness and confusion among those who take it. It's main uses are actually for depression, anxiety and insomnia. Doxepin is an interesting drug because although it technically is a H1 antagonist, it shares properties with a class of antidepressants know as tricyclic antidepressants, which may explain it's effectiveness in treating depression. A low dose of Doxepin was recently approved in 2010 for the treatment of insomnia and goes under the trade name Silenor.
- Diphenhydramine - One of the most common antihistamines and is included in numerous brand name medications over the counter such as Benadryl. Although an effective antihistamine, it's more common use is to induce drowsiness as a sleep aid. Diphenhydramine is the medication to use in an allergic reaction situation due to it's potency.
- Dimenhydrinate - Another very common antihistamine used in sleep aids and combination cold medications. It is also the ingredient in Dramamine which is used for motion sickness.
- Doxylamine - This one is not included in the chart above but is very similar to both diphenhydramine and dimenhydrinate. Look at the ingredients in your night time cold medication or sleep aid and it's almost a guarantee that it contains either diphenhydramine, dimenhydrinate or doxyamine!
- Chlorpheniramine - This drug is also a very common over the counter antihistamine. It's common in brands such as chlor-trimetron. It's similar to diphenhydramine (Benadryl) in duration of action (lasting about 4-6 hours) but tends to cause a little less sedation.
- Hydroxyzine HCL & Pamoate - These both are Rx products only. Although the same chemical, it comes in two different salt forms which historically have been used for two different indications(uses). It is thought that the HCL version does not cross into the brain and therefore is not associated with the sedation of the pamoate salt. Therefore the HCL version is typically prescribed for itching and allergies while the pamoate version is prescribed for anxiety (since it causes sedation).
- Meclizine - Both OTC and Rx, this antihistamine is the ingredient in Dramamine Less Drowsy as it tends to cause less sedation than dimenhydrinate but may not be quite as effective. The prescription version comes in a strength twice that of the OTC version.
- Promethazine - A common ingredient in prescription cough medications that include codeine. It's a fairly sedating antihistamine that does a good job of reducing mucus secretions as well.
Second Generation Antihistamines

Comments On Second Generation Antihistamines
- Loratadine (Claritin) - The first of the prescription second generation antihistamines to go over the counter. It is also the least expensive. This is a great choice to try first for your allergy symptoms since it is almost completely non-drowsy and works for 24 hours
- Cetirizine (Zyrtec) - Cetirizine was the second of the second generation antihistamines to go over the counter. The only drawback of this medication is that is causes drowsiness in ~5-10% of people and therefore is NOT marketed or labeled as non-drowsy.
- Fexofenadine (Allegra) - The last of the formally prescription antihistamines to go over the counter. It has the fastest onset of action of the OTC allergy medications and is non-drowsy. The only drawback is that it is the most expensive of the 3.
- The Other Prescription Products - There really is no need to discuss to other antihistamines that are prescription. They are uncommonly prescribed and very similar to their OTC counterparts.
Which Antihistamine Is The Best?
- When you go shopping for your allergy medicine and look at the OTC antihistamines, we at PharmacistAnswers.com recommend going with a second generation antihistamine. Most don't cause drowsiness and are long acting.
- We recommend Claritin (Loratadine) as your first option. It is non-drowsy, works for 24 hours and is very inexpensive.
- We recommend Allegra (Fexofenadine) as your second option if you find the Claritin (Loratadine) ineffective. It is a little more expensive, but it may be more effective and again is non-drowsy.




