
Overview
Fish and krill oil supplements are two of the most popular over the counter products on the market today. They both contain beneficial fatty acids and claim to support our cardiovascular health, cholesterol levels and much else. In this article, we explore both products and discuss the similarities and differences between the two.
It has long been a dietary recommendation that we consume fish regularly, as fish contain heart healthy omega-3 fatty acids. Marine omega-3s have a large body of evidence for cardiovascular benefit. However, many people have difficulty eating fish consistently, especially if they don't enjoy the taste. Due to the lack of fish in many of our diets, we often turn to supplements for our omega-3 needs.
People often are confused about what to look for in a fish oil supplement as well as possible alternatives, such as krill oil. Both fish oil and krill oil contain omega-3 fatty acids, which studies have shown can improve our cardiovascular health. While similar, fish oil and krill oil have significant differences which we detail below.
Fish Oil
The purified fish oil in supplements contain omega 3 fatty acids, specifically high concentrations of DHA (Docosahexaenoic acid) and EPA (Eicosapentaenoic acid). While fish oil supplements contain other types fatty acids (e.g. Omega-6 etc...), it is DHA and EPA that are the most well studied to provide cardiovascular benefits. As such, it is important to look for those two on the label of your product.
The concentration of DHA & EPA in fish oil products depend on the manufacturer and the process they use to purify their product. On the nutritional label, you will want to pay attention to 2 key pieces of information:
- Omega 3 Strength (Total Omega-3s)
- EPA & DHA Strength Fish Oil
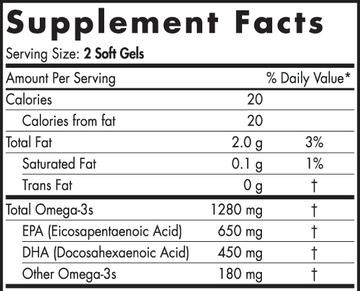
On the label above, from a popular fish oil supplement, we can see that one serving contains 1280 mg of total omega-3s. Of this, 650 mg is EPA and 450 mg is DHA. The rest of the omega-3's listed on the label are omega-3 fatty acids other than EPA and DHA that naturally exist in fish oil in low levels.
These “other omega-3s” include DPA (docospentaenoic acid) and ETA (eicosatetraenoic acid). While beneficial, it is the EPA and DHA that have the most benefit for cardiovascular health.
Lower quality fish oils tend to have a low concentration of EPA & DHA in relation to the total omega-3 content. Some low quality fish oils will also list 'fish oil concentrate' as an ingredient which typically contains a low percentage of omega-3s and an ever lower percentage of EPA & DHA. It is important to be aware of how your fish oil product is labeled. The example below is marketed as having "1000mg of fish oil per serving!"

Some people get the wrong impression with labels that state 'fish oil concentrate'. This doesn't mean 1000 mg of omega-3s... far from it actually. We can see on this label, that has 1000 mg of fish oil concentrate, only contains 300 mg of omega-3's and only 250 mg of EPA and DHA combined! Always pay attention to the label of fish oil products!
Aside from the high concentrations of EPA and DHA in most products, fish oil tends to be much less expensive than krill oil and they have a larger body of evidence for cardiovascular benefits. On the negative side, many fish oil products have very large capsules that can be hard to swallow and may cause some to have a 'fishy burp', but that is typically more common with lower quality products.
Krill Oil
Krill are very tiny shrimp-like crustaceans that are a major food source for many large ocean animals such as whales and sharks. Just like fish oil, krill oil contains omega-3 fatty acids, specifically EPA and DHA. The main difference is the concentration of EPA and DHA. The concentration of EPA and DHA is far less in krill oil vs. fish oil. As an example, below is an image of one of the most popular krill oil supplements, Mega Red.

We can see that 300 mg of krill oil only contains 45 mg of EPA and 27 mg of DHA, a far smaller concentration and amount than most fish oil supplements. Manufacturers of krill oil often advertise that the omega-3s in krill oil are better absorbed because the omega-3s are in a different chemical form. There is in fact some evidence that this is true and there have been studies that suggest that krill oil can lower cholesterol and triglycerides, just like fish oil. However, there's much better evidence that fish oil can lower cardiovascular risk. Krill oil also tends to be much more expensive than fish oil.
Krill oil does have some benefits over fish oil. The capsules are much smaller than fish oil capsules. Large capsule fish oil products can be difficult to tolerate for some people. If this is the case for you, krill oil may be a good option. Krill oil also doesn't have the 'fishy burp' associated with it. If you get easily nauseated from fish oil, krill oil may be better tolerated.
Conclusion
Fish Oil Pros
- High Concentration Of DHA & EPA
- Large Body Of Evidence For Improving Cardiovascular Health
- Less Expensive Than Krill Oil
Fish Oil Cons
- Large Capsules
- Fishy Burp In Some People
- Large Discrepancy In Quality Of Products
Krill Oil Pros
- Small Capsules
- No Fishy Burp
- Well Absorbed
Krill Oil Cons
- Low Concentration Of DHA & EPA
- Less Evidence Of Cardiovascular Benefits Vs. Fish Oil
- More Expensive Than Fish Oil




